Let’s face it.
Your target audience might have a shorter attention span than a goldfish.
It’s kind of your cue to check out interesting commercials for them.
Commercials are still essential in the era of internet marketing for:
- Drawing viewers in
- Spreading brand messaging
- Increasing sales
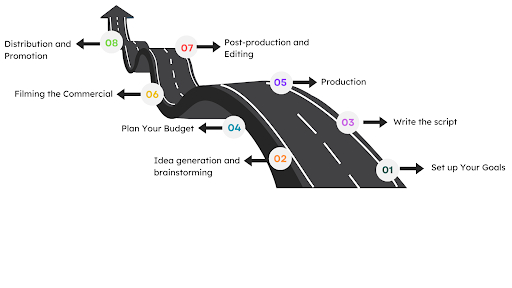
Let’s explore the entire commercial process today, from ideation to distribution.
→ Check out the 10 Best Commercials of All Time
| Highlights: A Step-by-Step Guide To Make A Commercial → Fixed Commercial Goal → Generate ideas and bring out the best script → Budget planning → Effective production strategies → Post-production steps and distributions |
What Is A Commercial?
A commercial is a form of advertisement. A great commercial or a promo video promotes your product or service.
Did you know that?
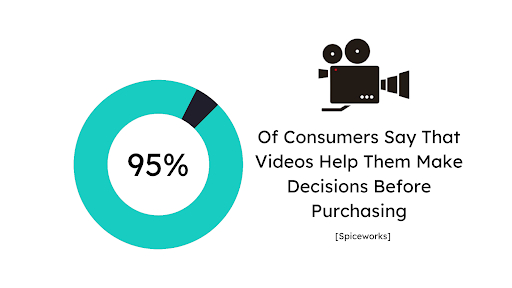
Imagine a world without commercials. No appealing tunes, enduring characters, or gripping stories. Commercials can mold our opinions, direct our decisions, and create a lasting impact.
Why Is It Important To Make A Commercial?
A great commercial is not made by accident.
Understanding your target audience, choosing the right media, and determining which KPIs are important. Moreover, mastering the technical aspects of making a commercial is all part of being an effective marketer.

It is crucial to make a commercial as it helps in:
- Building Brand Recognition
- Increasing Conversions
- Rise in SEO Ranking
- Increase in ROI
- Boosting Social Engagement
- Enhancing brand loyalty
- Reaching New Customers

The Power of Commercials
Nowadays, marketing is centered around commercials, which are captivating, memorable, and engaging. The influence of commercials is negligible.
People today lead such busy lives that they barely have time to watch long videos; unless the advertisements are really interesting. Furthermore, the cost of making them could be extremely high. So, the solution is to make your videos short.
73% of consumers prefer short-form videos to learn about products or services. [Source: Hootsuite]
Not just large brands are capable of creating engaging videos. It’s possible for you too. It also makes no difference how little your budget is. Short videos can still be created.
Additionally, you can keep prices down by expanding your business’s reach and sharing through the use of short films.
Key Aspects: Commercials remain a cornerstone of advertising for several reasons:
- Broad Audience Reach: They can use a variety of media, such as digital platforms, radio, and television, to reach a sizable audience.
- Impact on Emotions: Commercials can stir up intense feelings and establish enduring connections with companies.
- Measuring outcomes: You can look at analyses like ideas, clicks, and conversions to determine how effective they are.
- Originality: Commercials are capable of being altered to meet a variety of marketing objectives, such as pitching a product or developing brand awareness.
8 Steps to Make a Commercial: A Complete Guide
Making a commercial memorable should be your priority while learning how to make one. Consider advertisements that stick in your mind.
Step 1: Set up Your Goals
You should be clear about the goal and target audience of your commercial before you begin the whole process. This will supervise the whole manufacturing process and guarantee that the finished commercial satisfies your marketing goals.

Purpose of the Commercial
- Brand awareness: If increasing brand recognition and awareness is your goal, the commercial should focus on making a lasting impression.
- Sales: The commercial should emphasize the qualities, advantages, and special selling factors of the product to increase sales.
- Product launch: The commercial for a new product should create a sense of excitement and expectation.
- Event promotion: A commercial that highlights the main points of an event should entice viewers to watch it.
Audience Targeting
Remember that the attention span of your audience is limited. You have between 5-8 seconds to get your audience interested before shiny-object syndrome sets in. For this very reason, you must immediately capture their interest with a compelling hook.
- Demographics: To properly adjust the message, you must ascertain the target audience’s age, gender, geography, and interests.
- Psychographics: To establish more meaningful connections with individuals, take into account their values, lifestyles, and behaviors.
- Customer personas: You may better understand your target audience and adjust your messaging by creating in-depth profiles of your ideal customers.
Step 2: Idea generation and brainstorming
The next step in the commercial production process is ideation and strong concept creation. This phase decides the general direction of the commercial and lays the groundwork for the entire production process.
Generate Ideas
- Storyboarding: To make an appealing storyboard, visually represent the important shots and situations in your commercial. This will assist you in picturing the story’s progression and locating any possible obstacles.
- Research Your Rivals: Look through the best-performing commercials in your industry to identify trends and strategies. Look out for narrative methods, messaging strategies, and recurring themes.
- Generating Innovative Ideas: To generate a wide range of concepts, lead an unstructured brainstorming session. Consider using mind mapping or group brainstorming techniques.
Choosing the Right Concept
- Connection to the Audience: Ensure that the concept addresses and resolves the issues that your intended audience faces.
- Brand Unity: Check to see if the concept fits with your company’s mission, fundamental values, and visual identity.
- Quantifiable Goals: Set clear objectives for your commercials, such as increasing sales, generating leads, or brand exposure.
Storytelling
The best way to communicate your brand message to the end consumer is through a commercial that tells a great story.
A well-written story can pack pages of data into minutes. You need to evoke the feelings of the viewer so that they can relate to how a product can come of use in daily life.
If you have a product that solves a problem you can show many scenes showing your product’s use case.
- Emotional Connection: To build rapport, appeal to your audience’s feelings.
- Call to Action: Clearly state the action you would like the audience to take after seeing the commercial.
Define Your Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
At the core of a successful commercial is a clear and compelling (USP). Your product should clearly answer why a customer should choose your brand over others.
This advantage should be central to the message you want to convey. The USP should also be communicated concisely so that the viewer can understand the message you want to convey.
KISS Principle (Keep It Simple, Stupid)
When writing the underlying message, follow the KISS principle. Just make sure the message is concise, as overcomplicating it can negate the whole purpose of a commercial. Focus on a single, powerful idea that aligns with your USP. The goal is to leave a lasting impression without overwhelming the viewer with unnecessary details.
Step 3: Write the script
A careful balancing act between inventiveness and clarity is needed when crafting an engaging commercial script.
Checking Script Writing Fundamentals
Typically, a commercial script has three primary parts:
- Hook: The first sentence or scene that draws in the audience and establishes the mood of the advertisement.
- Body: The primary narrative or message outlining the advantages and value proposition of the good or service.
- Request for action: A clear and persuasive message that encourages readers to visit your website or buy something, for instance.
- Relatable Read: How to Write a Script for a Short Film?
Keeping Clarity and Creativity in Check
- Keep it brief: Since commercial scripts are usually brief, each word matters. Make an effort to communicate your point succinctly and effectively.
- Make effective use of images: Images can amplify your message and increase the interest level of your commercial.
- Speak casually: Compose your screenplay as though you were addressing the audience directly.
- Draw attention to advantages: Don’t just list characteristics; instead, concentrate on the advantages that your product or service provides.
Editing for length and flow
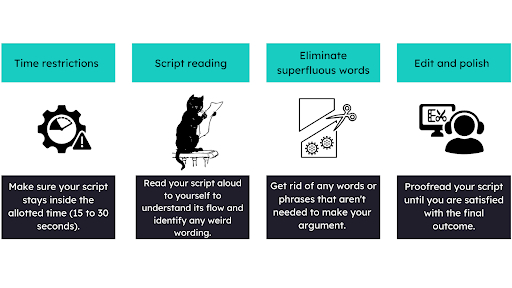
Step 4: Plan Your Budget
Only a well-planned budget can ensure the success of a commercial project. By carefully weighing the related fees, you may allocate your resources more effectively and avoid unanticipated expenses.

Budget Breakdown
- Talent: Casting directors, producers, and other workers will pay varying sums based on the talent’s location and experience level.
- Studio site: The cost of renting a studio space, site fees, and clearances may increase.
- Equipment: Costs for cameras, sound, lighting, and other production-related things can mount up.
- Post-production: You may need to pay more for color correction, sound design, visual effects, and editing.
- Distribution: The cost of distributing your advertisement across a range of media, including social media, online platforms, and television, will vary depending on the platforms and reach you choose.
Money-Saving Tricks
- Use internal talent: By making use of individuals who possess the necessary talents, your organization may be able to cut costs.
- Instead of purchasing, think about renting: Equipment rental could be more economical for one-time jobs.
- Rate-negotiating: To obtain the greatest offers, don’t be scared to haggle with vendors and retailers.
- Investigate other locations: Consider filming in less expensive locations to save money.
- Get ready ahead of time: By planning your production ahead of time, you can ensure a more productive workflow and avoid unforeseen expenses.
Allocating Resources
- Production vs. Distribution: To ensure excellent audio and graphics, allocate a significant portion of your budget to production. Don’t discount the distribution cost, though, if you want to ensure that your advertisement reaches the target market.
- Contingency fund: Remove a portion of your budget to pay for unanticipated expenses or changes to your production schedule.

Step 5: Production
Production entails arranging and arranging every component that will come together to form your finished video.
→ Check Out Our Detailed Video Production Process
Casting Talent
- Search for the target audience: Learn about the demographics and psychographics of the people you want to reach.
- Investigate possible actors: Seek performers who can successfully communicate your message and fit the image of your brand.
- Think about voice overs: If you don’t require actors to appear on camera, you might want to hire a voice actor.
Location Scouting
- Explain your idea: Establish the general style and tone of your video, taking into account the environment and mood.
- Areas: Look for places that fit your concept and are both reasonably priced and easily accessible when conducting your research.
- Think about inside vs. outside: Choose whether to film your video on-site or in a studio.
Scheduling and Permits
- Plan a shooting schedule: When choosing the dates and times of the shoot, take note of the actors’ availability along with the areas’ accessibility.
- Get the required permissions: If you propose to film in public areas or on private land, make sure you have the proper permits.
- Plan the logistics: Make essential reservations for housing, travel, and equipment rentals.
Step 6: Filming the Commercial
Hiring a Production Team
- Director: An accomplished director will direct the production and bring your concept to life. Seek out someone with a solid grasp of your intended demographic and a track record of producing commercial films.
- Cinematographer: A skilled cinematographer will guarantee the striking visuals of your commercial. Take a look at their commercial photography experience and portfolio.
- Sound Technician: A talented sound technician will record audio for your commercial that is crystal clear and of excellent quality. Seek out someone with a background in recording sound on-site.
→ Check out the Types of Commercials here.
Shooting Techniques

Tips for Efficient Filming
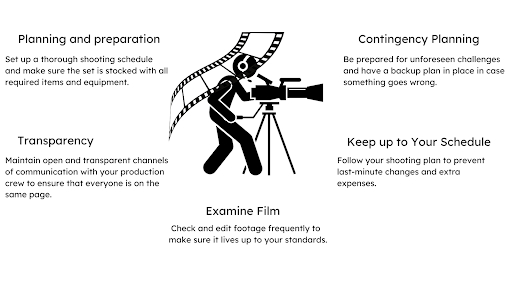
Step 7: Post-production and Editing
Your video comes to life during post-production. At this stage, you will edit your film, add music and visual effects, and make the final product look coherent.
Editing for Impact
- Cut out any unneeded video: Eliminate any video that doesn’t advance the plot or quicken the pacing.
- Include effects and transitions: To improve the visual interest and direct the audience through the video, use transitions and effects.
- Contrast: A professional and visually pleasing video can be achieved by adjusting the contrast and color.
- Proper audio levels: Make sure the audio is balanced and clear.
Incorporating Sound and Music
- Select suitable music: Choose music that fits the tone and message of the video.
- Include audio effects: Employ sound effects to set the mood and improve the viewing experience.
- Modify the volume of the audio: Make sure the audio is not overly loud or underplayed.

Review and Feedback
- Engage the parties involved: Distribute the revised video to the appropriate parties for their comments and approval.
- Make the required modifications: Consider comments and make any necessary final revisions.
- Seek expert advice: You might think about hiring a professional editor if you’re not sure about your editing abilities.
Just so you know, 78% of people trust reviews more than ads. [Source: Channel Signal]
Step 8: Distribution and Promotion
It’s time to release your commercial to the public after it’s finished. Selecting the appropriate channels for distribution is essential to connecting with your target market and making the most of your advertisement.
Choosing the Right Channels
- TV: When it comes to reaching a large audience, traditional TV advertising is still quite effective. Think about things like price, viewer demographics, and the viewing preferences of your target audience.
- YouTube: With a plethora of analytics tools and targeting choices, YouTube is a well-liked medium for video content.
- Social media: You may target particular demographics and track activity on sites like Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok.
- Streaming Services: To reach a certain audience, think about collaborating with streaming services like Hulu or Netflix.
Optimizing for Each Platform
- Video Length: Modify your advertisement’s duration to suit the platform’s limits and the preferences of your intended audience. Shorter films might be more effective on social media, while longer ones might be better suited for TV or streaming services. TV plays a crucial role in influencing people too.

- Resolution: Check that your video has a high definition for the best watching experience.
- Aspect Ratio: Pick the appropriate size ratio (that is, 16:9 or 4:3) based on the platform’s specs.
- Audio: Make sure your commercial’s audio is clear and understandable by optimizing its quality.
Ad Campaign Strategy
- Target Audience: Select the ideal group of people for the commercial and modify it accordingly.
- Budget: Decide how much you’ll spend on promotion and allocate it to the different media.
- Timing: Consider the best day and time of day to air your commercials.
- Analytics and tracking: Utilizing the information you gather from analytics tools, modify your advertising strategy as needed.
Paid vs. Organic Reach
You can promote your commercial through either paid ads or organic methods:
- Paid Ads: Options like PPC campaigns, social media ads, and sponsored content can give your commercial immediate visibility and precise targeting based on demographics and interests. This is perfect for product launches or reaching specific market segments quickly.
- Organic Distribution: Involves sharing your ad on non-paid channels like your website, YouTube, or social media profiles. This takes time to build engagement but can be more cost-effective and foster authentic connections with your audience.
A mix of both paid and organic strategies often works best to maximize reach and impact.
Timing and Frequency
When and how often you release your commercial can greatly affect its effectiveness:
- Timing: The best time to schedule your ad is when your target audience is most active. For example, TV ads during prime time or popular shows reach more viewers, while digital ads perform better during peak online times, like lunchtime or evenings.
- Frequency: Balance is key—too few airings may not be memorable, while too many can cause fatigue. Do some A/B testing to find the best timing and frequency and use data-backed analytics to monitor and adjust your strategy.
3 Common Mistakes to Avoid
Form common pitfalls of commercials are:
1. Overcomplicating the Message
One frequent mistake in making commercials is trying to pack too much information into a short time frame. Ads with multiple messages can overwhelm viewers and dilute the impact. The most effective ads focus on a single central idea that resonates with the target audience.
Avoid highlighting every product feature or benefit; instead, concentrate on one or two key points that are most relevant to your audience. Keeping the message simple and clear ensures it sticks with viewers and enhances the ad’s effectiveness.
2. Ignoring the Audience
A major error in ad creation is failing to tailor the commercial to the specific needs and preferences of the target audience. An ad that tries to appeal to everyone often fails to engage anyone. To avoid this, understand your audience’s demographics, interests, and pain points, and craft your commercial to reflect these insights.
You can do this by selecting the right visuals, audio, language, tone, and message. Ads that don’t connect with their intended audience can feel generic and disengaging. Customizing your ad’s approach helps build a stronger connection with viewers and encourages them to take action.
3. Lack of a Clear (CTA)
Even a well-produced ad can be ineffective if it lacks a strong CTA. A CTA directs viewers on what to do next—whether it’s visiting a website or usually to make a purchase. Without a clear CTA, you risk losing potential engagement and conversions. It is best to keep the CTA direct, concise, and aligned with the ad’s objectives. It should be visually precise and easy to understand, so viewers know exactly what step to take next.
A Closer Look at Successful Commercial Examples
There are many well-known advertisements, but some stand out in particular due to their creativity, impact, and cultural effect.
| Here are a few instances: 1. Brand Video Social Cutdown – Coffee Bay 2. Human Society of Truckee 3. Acuity Optical – Commercial |
To have the best deals on making commercials for your brand, check out Local Eyes Video Production.

Wrap Up: Commercial Video Making Process
A thorough understanding of your target demographic, inventive execution, and meticulous planning are necessary for producing a great ad.
Remember that a skillfully written commercial is more than simply a promotional tool; it’s an effective narrative tool that can captivate your target audience.
Now get your hands dirty, express your inner creativity, and begin producing ads that genuinely stand out.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How can a commercial be created step-by-step?
Which five processes are essential to writing a successful advertisement?
Is there a detailed guide available for running Facebook ads?
What is the first step in creating a commercial?
How do I choose the right platform for my commercial?
What are the key elements to focus on during ad production?
How can I measure the success of my commercial?

Founder at LocalEyes Video Production | Inc. 5000 CEO | Emmy Award Winning Producer









